Galvanized wire mesh is a versatile material widely used in various applications, such as fencing, construction, and industrial settings. The gauge of galvanized wire mesh plays a crucial role in determining its strength and durability. Understanding the relationship between gauge and these qualities is essential for selecting the appropriate wire mesh for specific projects. In this article, we will explore how the gauge of galvanized wire mesh affects its strength and durability, providing insights into making informed decisions when choosing wire mesh for different applications.
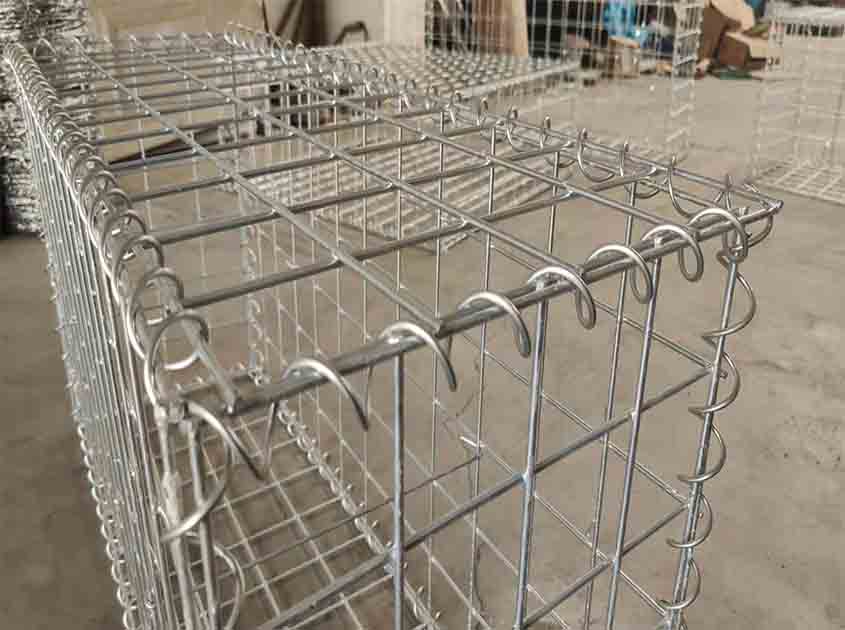

Understanding Wire Gauge:
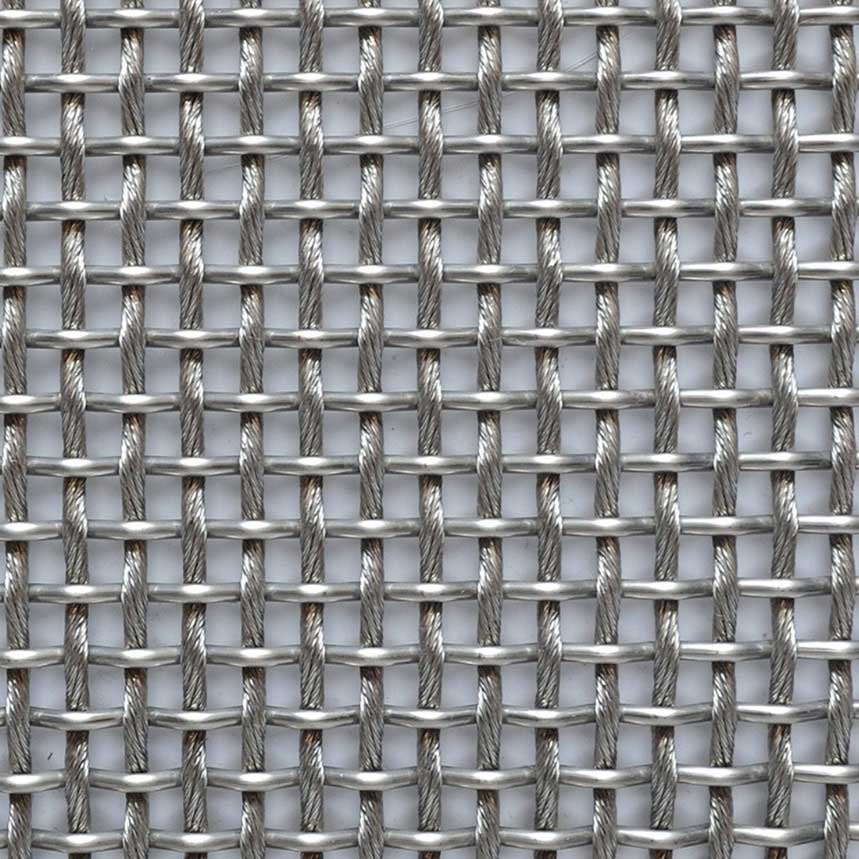
Wire gauge refers to the thickness of the wire used in the construction of galvanized wire mesh. It is typically denoted by a numerical value, with lower gauge numbers indicating thicker wires. For example, a lower gauge wire, such as 10 gauge, is thicker than a higher gauge wire, such as 16 gauge.

Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity:
The gauge of galvanized wire mesh directly impacts its strength and load-bearing capacity. Thicker wires used in lower gauge mesh provide increased strength, allowing the mesh to withstand greater tensile forces and resist deformation. This makes lower gauge wire mesh more suitable for applications requiring higher levels of strength and stability, such as heavy-duty fencing or structural reinforcements.

Durability and Longevity:
The gauge of galvanized wire mesh also influences its durability and longevity. Thicker gauge wires generally offer better resistance against physical impact, weather elements, and environmental factors. The added thickness enhances the mesh's ability to withstand stress, reducing the risk of breakage, sagging, or premature wear. As a result, lower gauge wire mesh tends to have a longer lifespan and requires less frequent maintenance or replacement.


.jpg)




.png)